Our News
Contact Us
- Tel:0086-135 8771 2673
- Tel:0086-135 8771 3265
- Email:sales@shenler.com
- Address:No.666 East Jiaotong Rd.,Wu'niu Street,Yongjia,Wenzhou,Zhejiang,China
6 Common Solid State Relay troubleshooting: Causes & Solutions
News | Feb 26,2025
SSR devices outperform mechanical relays due to their functionality and reliability; however, like anything else in an entire operational system, SSRs can and will fail. This article outlines the 6 most common solid state relay troubleshooting with SSRs, discusses associated root causes, and proposes solutions aimed at improving system performance.
What is a Solid State Relay?
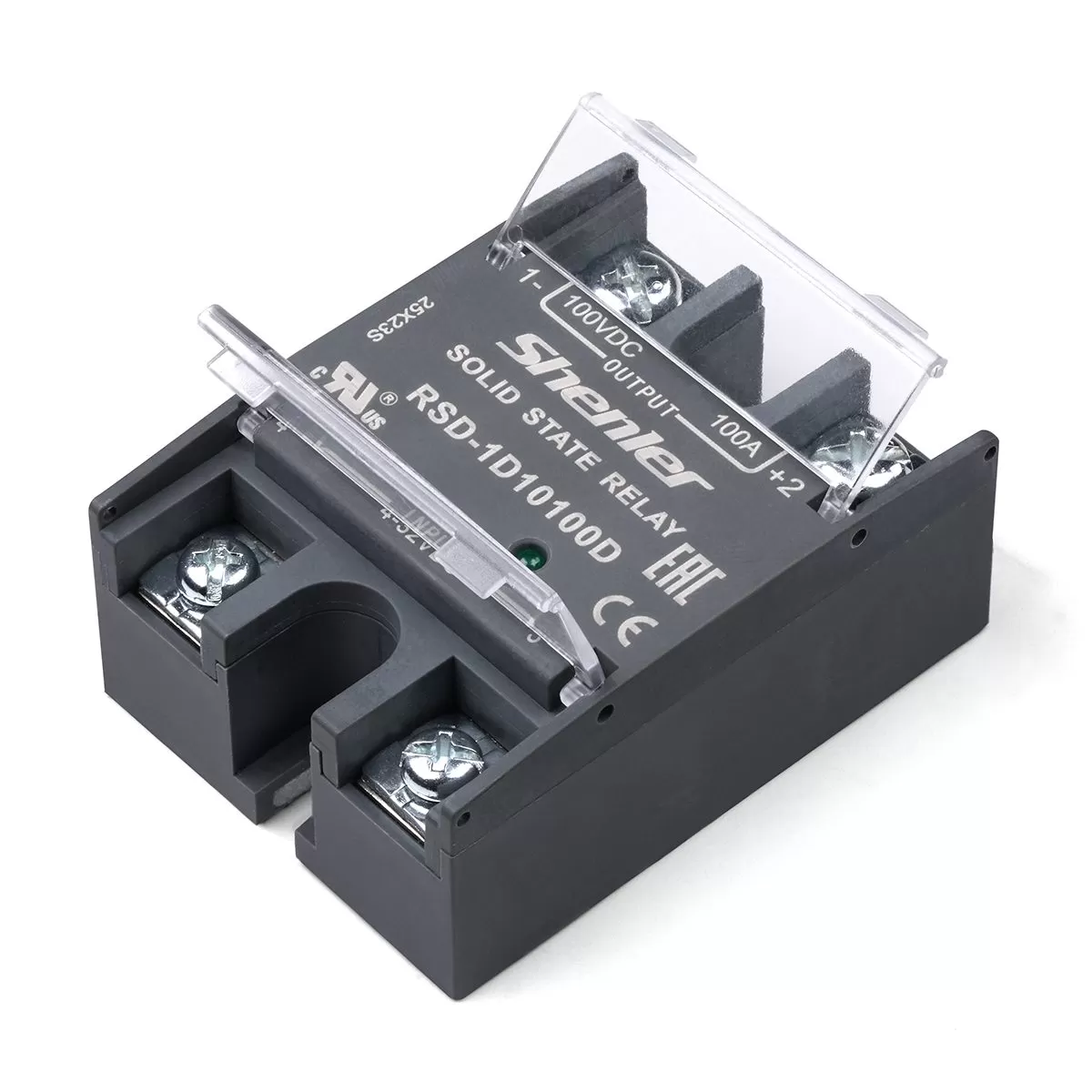

An SSR does not use mechanical parts to turn on a current; instead, it utilises parts from a semiconductor, incorporating a transistor or thyristor, to actuate an electronic switch. While electromagnetic relays are structured around moving parts, solid state relays incorporate neither, thus further improving their functionality and durability.
Symbol of Solid State Relay
IIn electric circuits, the symbol of solid state relay typically has these features:
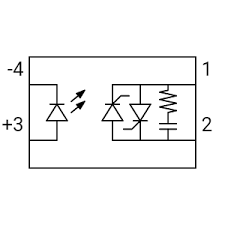
- The Relay’s Rectangle Body: The body of the relay also serves as a crucible container.
- Control LED Input: A visual indicator signifying that control is exercised or produced.
- An Output Section: A section that outputs signal information, which may vary depending on the kind of SSR.
LED serves as input while the output is a thyristor or transistor in most cases. All SSRs have unique symbols and identifiers that describe their capabilities, for instance, SSRs that work with an AC or DC load.
How to Tell if a Solid State Relay is Bad?
To check if a Solid State Relay is faulty, you can:
- Look for burn marks or other signs of damage.
- Check the LED on the input side with a multimeter diode. If the LED does not light up, or the output does not respond, the SSR may be defective.
- Randomly switch SSRs. Erratic switching could be due to voltage spikes or faulty semiconductors.
Can a Bad Relay Cause a Short?
Yes, a defective SSR can definitely cause a short circuit. This is particularly the case when the semiconductor devices on the output side are damaged. Take, for instance, a transistor or a thyristor which can result in a short and cause an unbounded current flow.
6 Key Solid State Relay Troubleshooting
| Issue | Description |
| SSR Not Working | Possible causes: overcurrent, overvoltage, insulation failure, improper rating, or wiring issues. |
| SSR Stays On | Possible causes: residual voltage, leakage current, inductive noise, overcurrent, or overvoltage. |
| Overheating | Caused by excessive current, poor connections, improper installation, or high ambient temperature. |
| Overcurrent | SSR current exceeds its rated capacity. |
| Overvoltage | Voltage spikes or incorrect power supply can damage the SSR. |
| Leakage Current | Small current leak even when SSR is off. |
Solid State Relay Not Working
Reasons of the Failure
SSR failure to respond even with the control signal indicates that there can be a fault at the output elements. Some possibilities for this failure are:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Explanation |
| Overcurrent | Excessive current passing through the relay | Too much current can damage the internal components of the relay. |
| Overvoltage Damage | Voltage spikes (surges or electrical faults) | Voltage spikes can damage the relay’s internal parts. |
| Insulation Breakdown | Insulation inside the relay degrades over time or with heat | The insulation can fail, causing the relay to malfunction. |
| Improper Rating | Relay is not rated for the load it’s controlling | If the SSR is mismatched to the load, it may not operate properly. |
| Wiring Issue | Loose or incorrect wiring | Bad connections can prevent the relay from receiving signals or power. |
How to Solve a Solid State Relay Not Working?
When the Solid State relay fails to work, it will compromise the protection of your equipment or system. To resolve this issue:
- Check and Replace Protection Devices:Fuses and other protective devices that are used as certain components must be checked to ensure that they are undamaged and also in working order.
- Verify Wiring: all the wires must be in good condition, and power should be supplied correctly; alternatively, a simple tape can be used on any loose wires to prevent any disruption to the relay.
Solid State Relay Stays On
Causes
The Solid State Relay (SSR) remains on even after the power input is disconnected. It is likely the case of a short circuit in the load circuit or a reset fail. This issue is often confronted during diagnosis and can result from several different causes like:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Explanation |
| Residual Voltage | Leftover voltage in the load circuit | Even without input power, leftover voltage can keep the relay on. |
| Leakage Current | Leakage current on input or output side | Small current passing through the SSR can keep it on. |
| Inductive Noise | Electromagnetic interference (EMI) or noise from nearby equipment | External noise can cause the relay to turn on falsely. |
| Overvoltage Overcurrent | Damage from too much voltage or current | Excessive voltage or current can damage the SSR, causing it to stay on. |
How to Solve a Solid State Relay Stays On?
- Install Protection Devices: Enhance relays with protection units such as varistors, snubbers, and branching surge arresters which block any voltage or current spikes.
- Ensure Clean Power Source: Keep the supply of power to the load uncluttered and steady so that there are no unwanted noise or fluctuations.
What Happens if Solid State Relay is Overheating?
Heat buildup is a common concern with Solid State Relays and may arise from multiple factors. If not properly dealt with, solid state relay overheating can destroy or incapacitate the heating element, thus putting your system at risk.
Causes of Solid State Relay Overheating
| Issue | Possible Cause | Explanation |
| Excessive Current | Current exceeds SSR’s rated capacity | Too much current can generate heat and cause overheating. |
| Poor Connections | Bad wiring connections | Increased resistance from poor connections creates heat. |
| Improper Installation | Incorrect installation or unsuitable environment | SSR may not dissipate heat effectively if installed poorly. |
| Insufficient Heat Dissipation | Lack of cooling or heat management | Without proper heat dissipation, SSR can overheat, especially under load. |
| High Ambient Temperature | Operating in a hot environment without cooling | High surroundings temperature can cause the SSR to overheat. |
Solutions
To prevent solid state relay overheating or resolve the issue of solid state relay overheating stuck (when the relay stays on due to heat buildup), follow these steps:
- Replace With an SSR That Has a Higher Current Rating: The solid-state relay should always be rated for the constant current that your application requires. If that means, remove and substitute it with another solid state relay with a higher rating.
- Strengthen Connections: Ensure that all cables and wiring are tightly secured and there is no corrosion or any damage to the connectors and terminals that will lead to excessive resistance and subsequent overheating.
- Incorporate Further Protection Measures: Incorporate a varistor or other protective devices in the output circuit to suppress any voltage spikes that could cause overheating.
- Additional Measures of Protection: Include an SSR fuse on the output side to avoid surge current and subsequently overheating situations.
- Increase the Effectiveness of the Solid-State Relay Cooling: Use a heat sink and ventilation fan together with vents to increase the passive dissipation of heat. If necessary, increase the ventilation of the SSR’s surroundings to improve the thermodynamic effectiveness of the materials used.
Solid State Relay Overcurrent
Overcurrent occurs when the load current exceeds the rated current of the solid state relay (SSR). This condition can lead to damage, reduced performance, or even complete failure of the SSR. Solid state overcurrent relay situations often arise due to sudden current spikes or when an SSR with an insufficient current rating is chosen for the application.
Solutions
To prevent overcurrent from damaging your SSR, consider the following steps:
- Select the Correct SSR Rating: An SSR must be selected based on the rated demand of the load, taking into account the current limits for the specific load being powered. When load current varies, SSRs with higher ratings than expected should be selected.
- Make use of Overcurrent Protection: SSRs need to be overcurrent protected by current limiting fuses or resistors connected upstream of the SSR. The use of overcurrent protection devices ahead of the SSR relay will reduce the amount of current that the SSR relay receives. In addition, these overcurrent protective devices are used to restrict or disconnect current flow in cases where the current becomes excessive.
- The electric load current for the solid state relay (SSR) must be checked regularly to verify that it is within acceptable limits. It is critical to take appropriate measures if abnormalities are identified. This could include reducing the load range or replacing the SSR with a higher rated unit.
Solid State Relay Overvoltage
Damage to any of the internal components of the solid state relay (SSR) would lead to malfunction or complete failure of the SSR. There are a multitude of reasons as to why overvoltage could occur including excessive voltage due to sudden spikes or surges, or an incorrectly selected power supply. Overvoltage happens when the voltage at the input or load terminal of the SSR exceeds its rated cap.
Solutions
In order to prevent overvoltage from damaging the SSR, this advice should be taken into account.
- Incorporate an Overvoltage Protection Circuit: To protect against overvoltage, additional circuitry may be placed in front of the SSR. This is commonly achieved using a device called a varistor. The varistor serves the purpose by displaying low resistance when voltage is above a certain level, meaning that the voltage can be absorbed and the SSR will not be damaged. Placing a varistor in front of the relay will help limit the amount of spikes in voltage entering the relay.
- Mount a Surge Protector: Additionally to using varistors, surge protectors may be placed within the circuit to block any high voltage bursts resulting from external phenomena, for example, lightning or fluctuations in the power grid. They assist in achieving the desired voltage level for the SSR.
What Are the Typical Control Voltages for Solid State Relays?
Solid state relays, as a rule of thumb, have a defined range of control voltages that vary depending on their type. Controlled DC SSRs typically accept 4-32 VDC. The control voltage for AC controlled SSRs usually sits somewhere between 90 and 280 volts.
Solid State Relay Leakage Current
A small amount of current can leak even when the relay is off. This occurs because of the semiconductor nature of these kinds of materials.
Solution
- Small leakage current is usually harmless in most applications, but if the leakage current is too high, replace the SSR.
- Regularly check the SSR to ensure its leakage current is within safe limits.
Do Solid State Relays Leak Current?
Yes, solid state relays leak a small amount of current when they are in the “off” state. Usually this amount of current is very small and should not pose any problem in most cases; however, in some situations it could require attention.
How to Test a Solid State Relay?
- Input Inspection: Check if the input side’s LED is functional by verifying it with a multimeter in diode test mode.
- Output Inspection: Check the voltage or resistance on the output side with a multimeter to verify that the SSR is switching correctly.
Conclusion
As with anything else, Solid State Relays (SSRs) have their advantages and disadvantages. They have superb response times and great reliability, but they are tough to troubleshoot because of their hardware complexity.
An understanding of the SSR principles alongside proper Solid State Relay troubleshooting procedures can help avoid conditions such as overheating, overcurrent, and leakage currents. With proper maintenance and prompt replacements, the long-term stability and performance of your system will be guaranteed. With these principles in mind, it is easy to see why proper troubleshooting is the key to prolonged optimal operation of the SSR.
References
- Solid State Relay Problems and Solutions: The Ultimate Guide
- Solid State Relay Problems, Causes & Solutions
- Troubleshooting Solid State Relays
--- END ---




